Quick Tips for Logistics Professionals
- Customs codes or HS codes govern international trade in goods. The Combined Nomenclature (CN) and TARIC are the reference for European companies.
- Rigorous identification of HS codes enables importers and exporters to anticipate costs, streamline customs clearance and benefit fromadvantageous trade agreements with the EU.
- With the tightening of security rules and regulatory requirements on transport documents, integrating SH codes into your management system is a recommended practice for optimizing the management of transport, duties and taxes.
- It is important to to check and update your customs codes as nomenclatures evolve.
- Working with an experienced customs representative who knows your products secures your HS codes, streamlines the customs management of your products and secures your business.
Understanding Customs codes
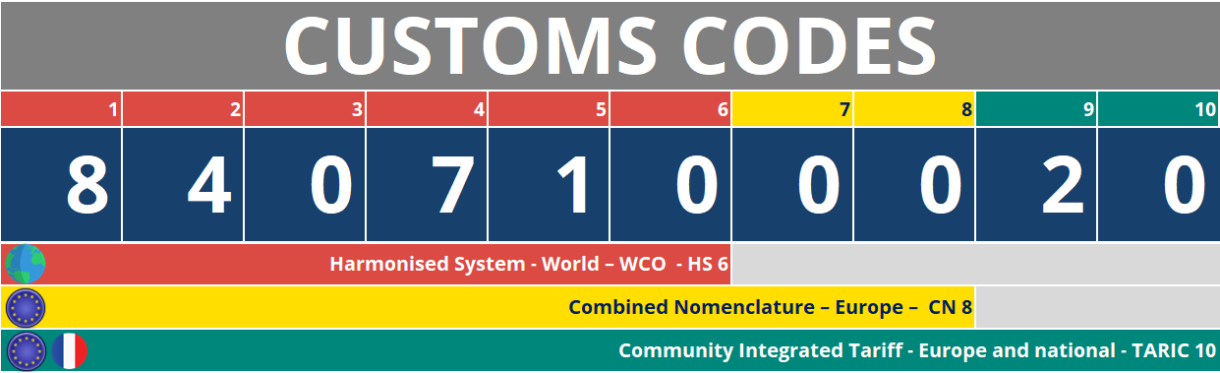
What is a HS 6, CN 8 and TARIC 10 code?
A customs code, also known as HS code, customs nomenclature or tariff classificationor customs tariff, commodity code or HS code is a numerical identifier assigned to each product traded internationally.
- It enables governments to monitor trade flows, regulate trade and collect customs duties, thus contributing to global economic and trade policies.
- This code enables operators to trade together even if they don’t speak the same language and belong to different economic systems. It identifies a commodity with a unique reference that can be interpreted in the same way by everyone.
There are several customs classifications, including :
- The Harmonized System (HS 6) of the World Customs Organization (WCO): used worldwide, it is based on a 6-digit structure.
- Combined Nomenclature (CN 8): specific to the European Union, this adds two digits to the HS for greater precision – 8 digits.
- The Integrated Community Tariff (TARIC 10): details the tariff and regulatory measures applied to goods imported or exported within the European Union.
Example of a customs code
8407 10 00 20 corresponds in the European customs code to spark-ignition reciprocating piston engines for the propulsion of land vehicles intended to be mounted on aerodynes which have themselves benefited from duty-free treatment or which have been built in the Community.
- 8407 10 (SH 6): the first four digits come from the Harmonized System (HS) and designate spark-ignition reciprocating piston engines.
The next two digits specify a sub-category, offering a further level of detail: engines for aviation. - 8407 10 00 (CN 8): the following two digits specify a sub-category within the European Union’s Combined Nomenclature (CN)
- 8407 10 00 20 (TARIC 10): these last digits are specific to TARIC and make it possible to integrate tariff or regulatory measures specific to the EU, in this case relating to duty-free treatment.
What are the reference documents and tools?
Here are 3 very useful tools at European, French and global level, and below are the main reference documents.
TARIC – EU Customs Tariff
RITA – French customs nomenclature
WCO Trade Tools – HS codes
European reference documents and tools
- TARIC (Integrated Tariff of the European Union) is a database integrating all EU customs and trade regulations. Accessible on the European Commission website, it is updated daily.
- The RITA (Référentiel Intégré Tarifaire Automatisé) database: a practical French tool for consulting national and European tariff regulations. Available on douane.gouv.fr.
- Combined Nomenclature (CN): the European version of the HS, this is the reference text detailing the 8-digit tariff headings, updated annually. Available on EUR-Lex, the CN is generally published at the end of October for entry into force on January 1.
Customs codes worldwide
- World Customs Organization (WCO) Harmonized System (HS): used by over 200 countries to harmonize trade. It is updated every 5 years. > > Access WCO.
- WCO Trade Tools database: a practical tool offered by the WCO to access international tariffs and regulatory measures. > Available on WCO Trade Tools.
How can you control and guarantee the reliability of your customs codes?
Customs tariffs play a key role in managing the flow of goods for companies, both for import and export, and contribute to both your financial rigor and the fluidity of your supply chain.
Why are HS codes important when trading with the EU ?
Importing goods into the EU :
- Identifying the HS code applicable to goods enables you to anticipate customs duties and VAT.
- The HS code is essential for customs clearance, reducing the risk of goods being blocked due to misclassification.
- The customs tariff can be used to check whether specific regulations apply (quotas, restrictions, health or technical standards).
For exporting goods out of the EU:
- HS codes guarantee the application of preferential trade agreements, when applicable, and avoids unnecessary costs for foreign customers.
- It secures customs declarations and reduces the risk of disputes with customs authorities in destination countries.
- It ensures regulatory compliance and reinforces the company’s credibility on international markets.
The importance of HS codes on transport documents
- With the entry into force of the new ICS2 (Import Control System 2) regulations in 2025 within the European Union, the transfer of HS codes onto transport documents such as LTAs(Lettres de Transport Aérien) becomes crucial: 6-digit HS codes on master LTAs and 8-digit HS codes on house LTAs.
- Similarly, with the introduction of ICS2 phase 3, theea carriers must provide a complete Entry Summary Declaration (ENS) before goods arrive in the EU, including, among other things, the 6-digit HS code . Phase 3 came into force in June 2024, with a transition until April 2025.
- The commercial invoice is a key document: ideally, it should include the HS code for each item. Although not compulsory, this indication on the invoice is essential to ensure compliance with customs procedures.
With the tightening of security regulations worldwide, it is becoming mandatory to include full HS codes on transport documents. Companies have an interest in integrating these HS codes into their ERP database to ensure end-to-end compliance and optimize their operations.
Why check your HS codes?
Checking and updating your customs codes against current customs nomenclatures ensures the reliability of data exchanged by your departments (Sales, Purchasing, Logistics, Customs and Accounting), ensures efficient customs clearance, and guarantees accurate payment of applicable duties.
Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- When importing, using an incorrect HS code will result in delayed customs clearance and additional costs.
- on export, lose a tariff advantage under a trade agreement due to incorrect classification, or mislead your buyer with the wrong customs code.
Best practices for efficient management
- It is essential toexploit official databases, such as TARIC and RITA, to refine tariff classification and avoid errors.
- Constant regulatory monitoring enables us to anticipate customs developments and adapt our practices accordingly.
- Applying proven analysis methods reduces the risk of incorrect coding.
Just as a company doesn’t change accountants for every invoice, it shouldn’t entrust its customs declarations to different service providers, depending on the flow!
Working with an expert freight forwarder who knows your products and understands your nomenclature makes customs clearance much smoother, and ensures reliable management of your customs tariffs in terms of fees, taxes and duties.
More information on customs codes and tariffs
- Customs codes: what you need to know when trading with the EU
- How to check your customs codes and tariffs in 2025?
- Check the changes in European Union tariffs in 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023, 2024.